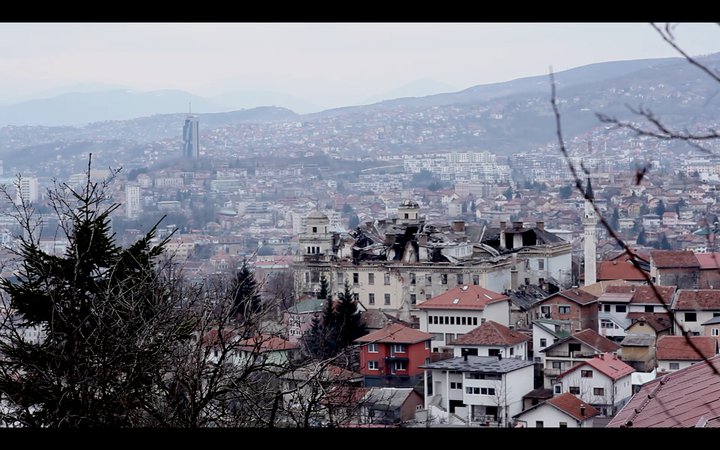
The fighting ended long ago, but it would be a stretch to say the country is at peace.
Today, when you ask people in my country if they live in peace, most will answer that they do. But if I defined a state of peace as freedom and a sense of security, I suspect they would answer negatively. They equate peace with the fact that there is no active fighting, but to be a peaceful nation where there is harmony and accord among people, is another matter.
Bosnia-Herzegovina is a country whose land and people are divided, separated into two entities — the Republika Srpska and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina — and the independent Brčko district. The political makeup draws heavily from the boundaries imposed by the Dayton Peace Accords of 1995, allowing little freedom for change. Bosnia is a democracy, but the needs of the people are often ignored.
There are different stories and truths that make up a confusing history; children of different ethnicities are taught from different textbooks, each with its own stance on history and fact. This difference in opinion concerning memory and the past is a huge stumbling block to future advancement and social progression.
The war in the region ended almost 20 years ago, and those who were affected by the turmoil have slowly managed to stitch their lives back together. The younger generation, born after the war, would rather forget the past; they did not live through the horror and are quick to dismiss the trauma it left behind. Their judgment and outlook is colored by the experience of their immediate family, which can create a problem when it comes to questions of equality and integration.
After the fall of Yugoslavia and the war, nationality — the sense of who and what you are — became more important. During communism, Yugoslavia was secular; people neither knew nor cared about the ethnic origins of their neighbors. With the explosion of nationalism and war, ethnicity took center stage and still infuses day-to-day life.
It is difficult to step outside the confines of your own name and nationality, and to suffer condemnation as well as subtle prejudice from your colleagues, fellow citizens and peers. In Bosnia, it is hard to deny your origin, and if you choose to be nothing you will always face judgment.
Bosnia is still a developing country, a democratic creation that is slowly coming out of a long transitional period. There is still a great sense of shame attached to talking about personal trauma and people’s actions during the armed conflict from 1992 to 1995.
It is shameful and painful to admit that genocide took place in Srebrenica or to talk about the concentration camps around Prijedor or the Čelebići prison camp. It is considered dishonorable to admit that there were people, members of your ethnic group, who could commit such terrible crimes against innocent civilians. It hurts to admit that these people are a part of you, that you come from the same place. Today it is easier to join the collective blindness and denial and live in a world that recognizes only the facts that appeal.
What happens when you leave the comfort zone? When you step away from ethnically oriented policies and furnished histories, and choose to create a unique truth? Then you realize that Bosnia is a largely divided country and that you could be loved for your principles and attitude in one part of the country but hated in the other.
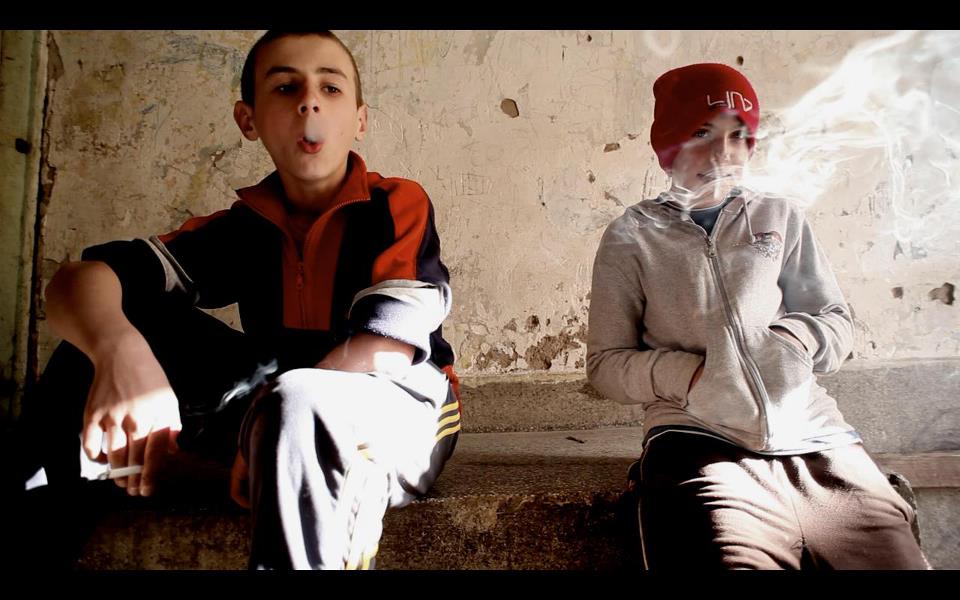

When a young person in Bosnia steps forward to admit the mistakes of “their” people, to vow not to forget the victims, regardless of their names and ethnicities, then that young person is branded a traitor, threatened with death, and accused of collaborating with “the others” to propagate lies.
From living under communism, in a secular society where we were oblivious to ethnicity, we have moved into an era in which a person’s name is more important than his or her morality. It is an age when people are not divided by their moral compass, their ability to do good or bad, but into “us” and “them”. People and communities are closing in on themselves, unable to look forward with a clear and unprejudiced mind. Among the young there is a resignation to the way things are, a feeling of helplessness to create change.
Bosnia’s development depends not only on its economy, but also on its people’s willingness to accept and acknowledge the past as well as the current dysfunctional political and social climate.
Bosnia’s tourism industry is blossoming. It is a country full of natural beauty and resources. We are beginning to forge a new name for ourselves, not defined by war.
But we must ask: “What do we want our children and grandchildren to remember? What life do we want them to have?” We want to create an atmosphere of harmony and equality — a sustainable peace.